Spiders are some of the most fascinating creatures in the animal world. Known for their eight legs, silk webs, and unique hunting skills, these tiny animals play an important role in nature. Many people think spiders are scary, but in reality, most are harmless and even helpful to humans. Mississippi is home to many different kinds of spiders, both indoors and outdoors. By learning more about them, we can better appreciate their value to the environment and learn how to live alongside them safely.
The Importance of Spiders
Spiders are like nature’s pest control experts. Every day, they eat insects such as mosquitoes, flies, and crop-damaging pests. Without spiders, insect populations would grow out of control, affecting farms, gardens, and even our homes.
Their silk is another amazing feature. Spider silk is stronger than steel by weight, yet light and flexible. Scientists study it to create better materials for things like medical stitches and protective clothing. Spiders also help keep ecosystems balanced, which means their presence often signals a healthy environment.
Mississippi’s warm climate supports a variety of spiders that thrive in gardens, forests, and fields.
Let’s talk about some of the most important parts of the spider.
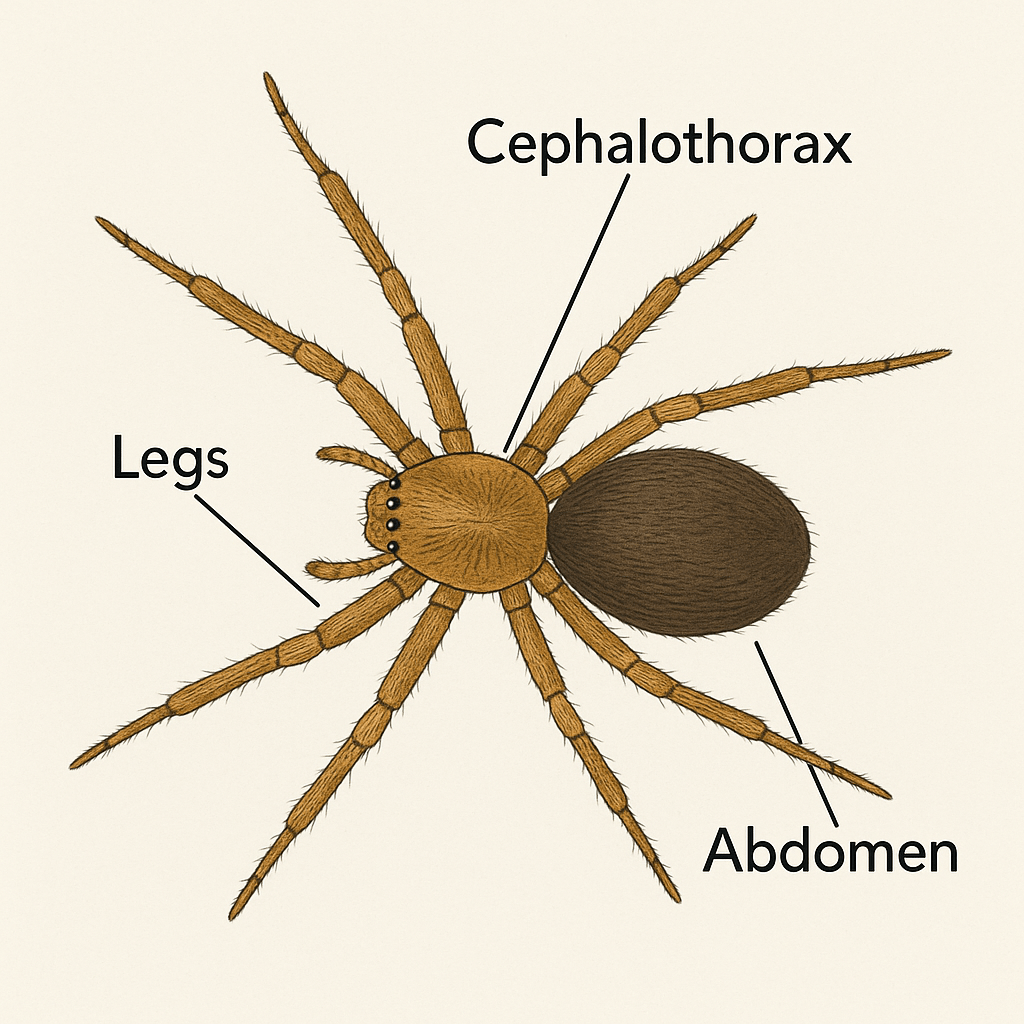
Explaining the Main Spider Body Parts
1. 🧠 Cephalothorax
The cephalothorax is the front section of a spider’s body. It’s basically the “head and chest” combined (called the prosoma in scientific terms).
Main features found here:
- Eyes – Most spiders have 8 eyes, arranged in different patterns depending on the species.
- Mouthparts – including the chelicerae (with fangs) for catching prey and pedipalps for sensing and feeding.
- Leg attachment – All 8 legs are connected to this section.
- Brain and nervous system are located here.
*The cephalothorax is covered in a harder outer shell (exoskeleton), giving it strength for movement and protection.
2. 🫁 Abdomen
The abdomen is the rear section of the spider’s body (scientifically called the opisthosoma). It’s softer and more flexible than the cephalothorax.
Main functions:
- Houses the heart, lungs, and digestive system.
- Contains the spinnerets at the end — silk-spinning organs that produce thread for webs, egg sacs, and movement.
- Expands when the spider eats or carries eggs.
*The abdomen is where most of the spider’s internal life functions happen. If you look closely, you’ll often see fine hairs or patterns unique to each species.
3. 🦵 Legs (8)
Spiders have eight legs, all attached to the cephalothorax — never the abdomen (that’s a big difference from insects!).
Features of the legs:
- Each leg has seven segments, giving spiders excellent flexibility and control.
- Sensory hairs cover the legs, helping spiders detect vibrations, air movement, and prey.
- Specialized claws at the ends help them climb webs and surfaces.
- Some spiders can move incredibly fast or even jump (like jumping spiders 🕺).
*The legs aren’t just for walking — they’re also the spider’s main tools for sensing the environment.
📝 Additional Important Spider Body Parts
Let’s go beyond the basics — these parts are smaller but very important to how spiders live and hunt.
🕸 1. Pedicel
The pedicel is the tiny waist that connects the cephalothorax and abdomen.
- It’s narrow but flexible, allowing the spider to move its abdomen freely while keeping the front steady.
- This is especially useful for web-building, silk spinning, and mating.
*It’s not always labeled in simple diagrams, but it’s a key anatomical feature.
🦷 2. Chelicerae and Fangs
Located at the front of the cephalothorax, these are the spider’s mouthparts used for hunting and defense.
- Chelicerae are small appendages that end in sharp fangs.
- Spiders use them to inject venom into prey, paralyzing it so they can feed.
- The chelicerae also help tear and hold food.
*Different spider species have different fang shapes depending on how they hunt.
🦴 3. Pedipalps
Pedipalps look like short extra legs near the spider’s mouth.
- They are not used for walking.
- Instead, they act like “feelers” to sense food and surroundings.
- In males, pedipalps are also used during mating to transfer sperm.
*Think of pedipalps as the spider’s “hands” and “noses” combined.
🧵 4. Spinnerets
These are tiny, finger-like organs at the tip of the abdomen, used to spin silk.
- Most spiders have six spinnerets, and each can produce different types of silk.
- Silk is used for making webs, wrapping prey, creating egg sacs, building shelters, or making draglines to travel.
- The silk starts as a liquid and hardens when pulled through the air.
*Spinnerets are one of the most unique and amazing spider features.
🦠 5. Sensory Hairs
Tiny hair-like structures cover the legs and body.
- They act like sensors, picking up vibrations, air movement, and chemical cues.
- Some are even sensitive to sound or smell.
- Spiders rely on these hairs more than vision to detect danger and prey.
*This is why spiders can react so fast even when you don’t see them looking at anything — they feel everything around them.
📝 Spider Body Parts — Multiple Choice Questions
🧠 Part A: Basic Questions
- How many main body parts does a spider have?
a) One
b) Two
c) Three
d) Four
- Which of the following is the front section of a spider’s body?
a) Abdomen
b) Spinnerets
c) Cephalothorax
d) Pedipalps
- Where are the spider’s legs attached?
a) Abdomen
b) Cephalothorax
c) Pedicel
d) Spinnerets
- Which part of the spider’s body produces silk?
a) Cephalothorax
b) Abdomen
c) Legs
d) Chelicerae
- How many legs do spiders have?
a) 4
b) 6
c) 8
d) 10
🧬 Part B: More Detailed Questions
- What are the small appendages near a spider’s mouth that help with sensing and feeding?
a) Spinnerets
b) Pedipalps
c) Chelicerae
d) Pedicel
- What is the name of the narrow “waist” connecting the cephalothorax and abdomen?
a) Spinneret
b) Pedicel
c) Mandible
d) Exoskeleton
- Which body part contains the spider’s heart, lungs, and silk glands?
a) Cephalothorax
b) Abdomen
c) Pedipalps
d) Chelicerae
- What do the chelicerae and fangs help the spider do?
a) Spin webs
b) Jump long distances
c) Inject venom and catch prey
d) Breathe underwater
- What are the tiny hair-like structures on a spider’s legs used for?
a) Decoration
b) Sensing vibrations and air movement
c) Spinning silk
d) Attracting mates

Now Let’s Explore Different Spiders!
One of the most eye-catching species is the Yellow Garden Spider (Argiope aurantia). These spiders build large, circular webs with a unique zigzag pattern. Many people call them “writing spiders” because their webs look like they have letters written across them.
The Golden Silk Orb-Weaver (Nephila clavipes) is another impressive spider. Females spin large golden webs that shine in the sunlight. Their silk is extremely strong, and their webs can stretch between trees or fence posts.
On the ground, Wolf Spiders (Hogna species) can often be spotted hunting at night. Instead of making webs, they chase down their prey using speed and good eyesight. A fun fact is that wolf spiders carry their babies on their backs after they hatch.
The Spiny Orb-Weaver (Gasteracantha cancriformis) is a tiny spider with a crab-shaped body and colorful spikes. Despite their fierce appearance, they are harmless and often brighten up garden spaces.
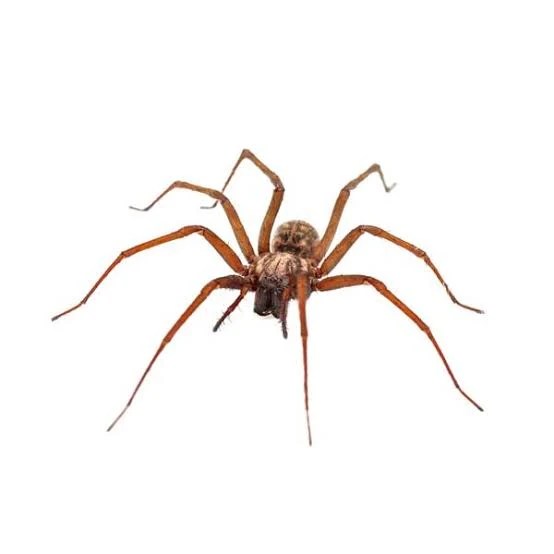
The Brown Recluse (Loxosceles reclusa). These spiders prefer quiet places like woodpiles and sheds. While they are not aggressive, their bites can be dangerous, so it’s best to avoid handling them..
Many spiders prefer living indoors where it’s dry and sheltered.
Cellar Spiders (Pholcus phalangioides) are often found in basements and ceilings. Their long, thin legs have earned them the nickname “daddy longlegs.” They gently vibrate their webs to confuse predators.
The American House Spider (Parasteatoda tepidariorum) is one of the most common indoor spiders. These small brown spiders build messy cobwebs in corners, behind furniture, and near windows.

Jumping Spiders (Salticidae family) are tiny but energetic. They use their excellent vision to stalk and leap onto their prey. They are curious and often turn to look directly at humans with their big front eyes, which many people find cute.

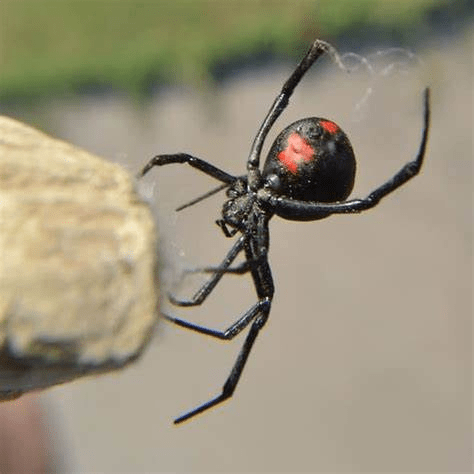
The Southern Black Widow (Latrodectus mactans) is a shiny black spider with a red hourglass shape on its belly. These spiders like quiet spaces such as garages and crawl spaces. Their venom is powerful, but they are shy and rarely bite unless disturbed.

Safety and Respect
Most spiders want to be left alone and will not harm people. However, it is wise to take simple precautions. Avoid sticking your hands into corners, shoes, or boxes without checking first. Shake out clothes or shoes that have been sitting unused for a while. Keeping your home clean and uncluttered discourages spiders from making themselves comfortable. If a dangerous species like a brown recluse or black widow is found, it may be best to ask an adult or professional to remove it safely.
Fascinating Spider Facts
Spiders are not insects; they have eight legs and two main body parts, while insects have six legs and three body parts. There are over 45,000 known spider species in the world, and new ones are still being discovered. Some spiders rebuild their entire webs every single night, showing incredible skill and patience. Most importantly, the majority of spiders are harmless and help make our world a healthier place.
Comprehension Check
Test your knowledge with these quick multiple-choice questions:
- What makes spiders different from insects?
a) They have wings
b) They have eight legs and two body parts
c) They can swim
d) They make honey - Which spider builds a golden-colored web?
a) Jumping Spider
b) Golden Silk Orb-Weaver
c) Wolf Spider
d) American House Spider - Which spider is venomous and should be avoided indoors?
a) Spiny Orb-Weaver
b) Cellar Spider
c) Southern Black Widow
d) Jumping Spider - Why are spiders helpful to gardens?
a) They eat insects that harm plants
b) They plant flowers
c) They dig holes for water
d) They chase away birds - Which of these spiders is known for jumping to catch prey?
a) Wolf Spider
b) Brown Recluse
c) Jumping Spider
d) Black Widow
Answer Key
- b
- b
- c
- a
- c
Final Note:
Spiders are often misunderstood, but they play an important part in Mississippi’s ecosystems. By controlling insect populations, creating strong silk, and signaling environmental health, they contribute to a balanced natural world. While it’s wise to be cautious around certain species, most spiders are harmless and helpful neighbors. Learning about spiders helps us respect and protect these amazing creatures rather than fear them.
Interested? Lets learn more with these fun videos: